ProTerra Standard and Regenerative Agriculture practices

Regenerative agriculture is a farming approach that aims at improving the health and biodiversity of the soil, enhancing ecosystems and consequently biodiversity, capturing carbon in the soil to mitigate climate change and conserving water. It helps to make farms more resilient and supports business development while contributing to the production of healthy and nutritious food.
Table 1 presents the definition of the four impact areas considered key to regenerative agriculture.
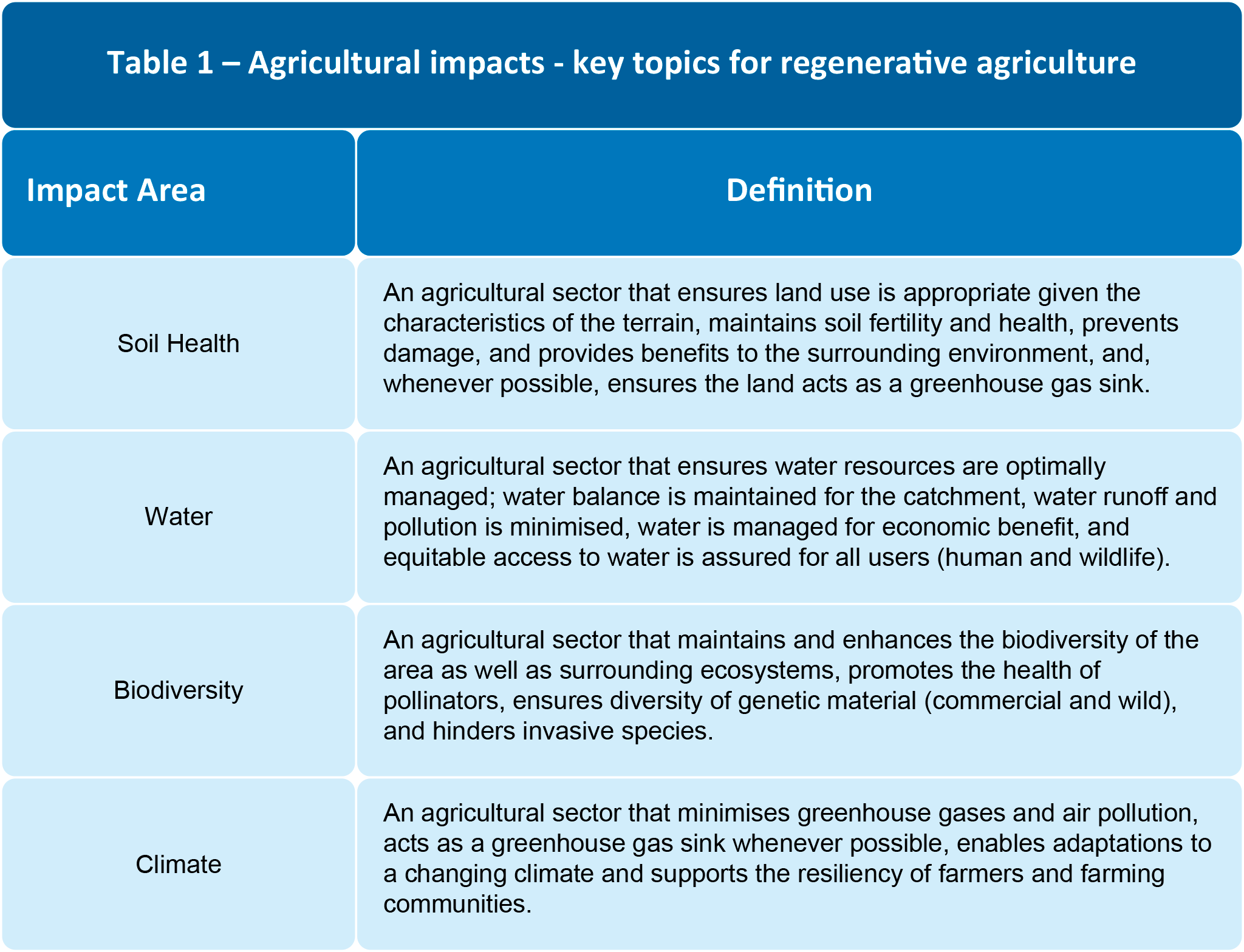
Source: September 2023 REGENERATING TOGETHER A global framework for regenerative agriculture/ SAI Platform 2023[1]
Unlike conventional farming which often depletes the soil and relies heavily on chemical inputs (pesticides and fertilisers), regenerative agriculture avoids or minimises the use of such inputs while using several other practices. These include:
- crop rotation;
- cover cropping;
- reduced or no tillage;
- integrating livestock into cropping systems;
- efficient irrigation and water use;
- wastewater treatment;
- pre-converted areas;
- riparian buffer areas;
- energy efficiency;
- energy from renewable sources;
- farm areas with trees, shrubs;
- nutrient management and
- pest management, among others.
The applicability or not of each of these practices varies according to the socio-economic and agro-ecological aspects of each farm.
The ProTerra Standard on Social Responsibility and Environmental Sustainability includes a number of elements in its requirements that are consistent with regenerative agriculture practices and ultimately lead to attaining the core objectives of regenerating the soil, promoting healthier ecosystems and more resilient agricultural systems.
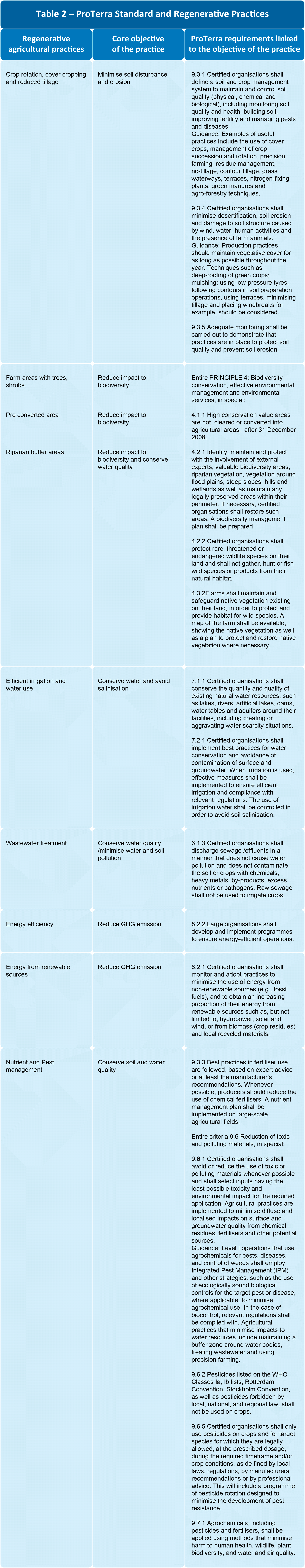
Table 2 correlates some of the key regenerative practices with several of the ProTerra Standard V5 requirements.